

Oct 8, 2025


Oct 8, 2025


Oct 7, 2025


Oct 7, 2025


Oct 7, 2025


Oct 7, 2025

Updated: Oct 28, 2025
Today, maps are more than just a guide. We can view weather conditions, traffic flow, disaster risks, and even social media activity in real-time. Thanks to modern online mapping services, this dynamic information gains meaning through constantly updated map layers. So, how do these systems work, and why should we choose one when developing a project?
In this article, I'll cover the basic principles of online mapping services, the installation and integration steps for these platforms, and share tips on which tools are best suited for each scenario. I'll compare popular systems like ArcGIS Online, Google Earth Engine, and Mapbox from an application developer's perspective.
This article isn't just a technical review; it also offers practical insights and new ideas for problems encountered in the field. If the future of real-time data interests you, let's get started!
Real-time maps can provide a clear and real-time view of what's happening at your current location. Who wouldn't want such a feature? ArcGIS Online is one of the most comprehensive platforms that meet this need. Developed by Esri, this cloud-based GIS system is accessible from a web browser or mobile device, allows you to print 2D and 3D maps, integrates with various data sources, and manages real-time data. This system allows you to monitor information like traffic, disasters, and IoT sensor data in real time on the map.
Getting started with ArcGIS Online is quite systematic: First, you create an organizational account. Then, simply select a base map with Map Viewer and import data via CSV, GeoJSON, Shapefile, or service layers. Once you've created your map, you can effectively present your data with solutions like Dashboards or Story Maps.
On the real-time data front, ArcGIS Velocity comes into play. This module allows data arriving via MQTT, Kafka, or HTTP feeds to flow instantly onto the map. Filtering, geofencing, and analysis can be performed through this flow. This allows you to instantly track the location of disaster response teams or any malfunctions in city infrastructure on the map.

One of its advantages is its versatility: it offers a secure and integrated framework designed for enterprise use. However, the learning curve can be steep for beginners. Its closed ecosystem can be limiting for some developers.
ArcGIS Online is one of the most organized and reliable ways to visualize real-time data. It's used by a wide range of people, from urban planners and disaster managers to IoT developers and academics. If you're interested in map-based decision support systems, this platform should definitely be on your radar.
Are you ready to explore the world with data? Google Earth Engine (GEE) is a cloud-based analytics platform that allows you to aggregate millions of images from space and transform them into meaningful information. With this system, you can explore solutions to major problems like climate change, deforestation, and urbanization right on your screen. This powerful tool, powered by Python or JavaScript, combines your engineering acumen with a planetary perspective.
To access GEE, all you need is a Google account and a short application. Then, you'll be greeted by the Code Editor, where you can start writing code and analyzing. You can incorporate satellite data like Landsat, MODIS, and Sentinel into your project with just a few lines of code. For example, you can track changes in vegetation by calculating NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index) using Sentinel-2 data. As you run your code, the map becomes dynamic, bringing the results to life with graphs, time series, and color overlays.
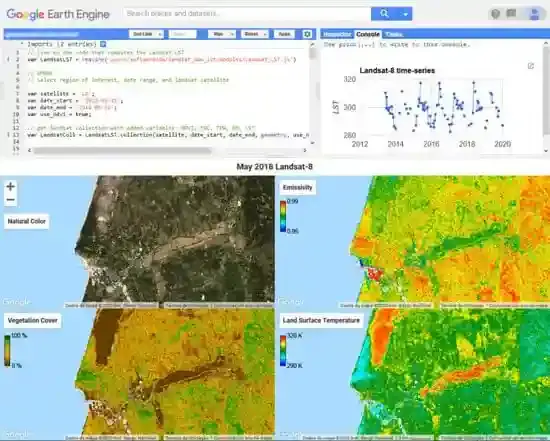
To get started, register with Earth Engine and open the Code Editor. Select the dataset you need from the Data Catalog and add it to your project. Display the data on a map with Map.addLayer. For big data analyses, you can extract summary information with reduceRegion or reduceWindow. Once you're done, you can export the results or share them as an interactive application.
Earth Engine is a true expert in environmental monitoring. It's used in a wide range of areas, from deforestation and climate analysis to land cover maps and fire detection. The machine-learning-powered Dynamic World dataset provides global land cover maps with a resolution of 10 meters. If you're curious about air pollution, you can look no further than the NO₂ data from the Sentinel-5P satellite. For urban planners, this platform is invaluable for monitoring urban green space loss or concreting.
GEE's biggest advantage is its free (academic/research) access to a massive catalog of satellite data and its ability to process this data quite quickly. However, remember, this tool is code-based. It uses code rather than visual interfaces. There's a slight learning curve for beginners; knowledge of Python or JavaScript is required. While we say real-time, the data is typically updated every few hours or days. Furthermore, commercial use may require separate licensing terms.
If you want to combine surveying engineering with data, and the environment with technology, Google Earth Engine invites you to a long but exciting journey.
Digital maps carry data that provides decision support. Placing this data on a map in a meaningful, interactive, and real-time manner is impossible with a standard system. This is where Mapbox comes in. It's a powerful and customizable platform that allows developers to combine data with aesthetics, freely shape design, and enrich the user experience in real time. It's a tool that gives data movement and context.

Mapbox is a modern platform that offers developers custom map, navigation, and search APIs. With Mapbox Studio, you can completely customize your map designs and integrate interactive maps into your websites with powerful JavaScript libraries like Mapbox GL JS. This system, which works with a raster or vector tile structure, provides fluid and dynamic visualization with high-performance WebGL support. You can integrate your geographic data in formats like JSON or GeoJSON as layers on the map, and you can completely define the visualization logic.
To get started, sign up for the Mapbox website and get your access key. Choose a pre-made map style from Mapbox Studio or create your own. Add the Mapbox GL JS library to your web app and initialize the map with new mapboxgl.map({...}). Easily add markers and layers.
For live data, you can dynamically bind data from the API to layers with feature-state, or keep the map up-to-date by updating the GeoJSON data with source.setData().
When it comes to creating customizable, user-specific maps that interact with real-time data, Mapbox is one of the most powerful choices. It's used in a wide range of scenarios, from tracking urban public transportation systems to bike park occupancy, from tourist area maps to real-time customer density analysis. Additionally, Mapbox plays a key role in in-game map designs and mobile traveler apps for game developers. For example, tracking global mobility has become crucial during the pandemic. Mapbox played a key role in COVID-19 maps, presenting data instantly and impressively.
Mapbox gives developers full control over their maps. It's fast, interactive, and visually powerful. It's ideal for those who want to build their own mapping experience from scratch.
However, if in-depth analysis is required, it won't do the job on its own. It may need to be supplemented by external libraries or server-supported systems. While the free usage quota is sufficient for small-scale projects, larger applications require cost planning. Furthermore, effective use of the platform requires basic technical knowledge of WebGL, API management, and map design.
If you work in fields like surveying, data visualization, or city analytics and are looking for a dynamic platform, Mapbox is worth exploring.
Real-Time Data Saves Lives: Coordination between field teams and headquarters is crucial during disasters like earthquakes and floods. ArcGIS Online and Velocity make this process manageable by displaying flight data, debris locations, and crew movements in real time. Mapbox is an effective choice for dynamic web maps for public information.

You can analyze local meteorological data with ArcGIS Online; create interactive maps with radar imagery and storm tracks with Mapbox. If you're working globally, Google Earth Engine (GEE) provides comprehensive analysis by processing satellite data from data centers like NOAA and Copernicus.
ArcGIS is powerful for aggregating and analyzing urban data such as population and infrastructure. Mapbox offers rapid prototyping and user-friendly visualization advantages for projects working with open data. GEE supports strategic decisions by tracking land use and heat island effects over time.

GEE is at the forefront of large-scale environmental issues like deforestation and water pollution. ArcGIS can instantly map air and water quality data from IoT sensors. Mapbox is an effective platform for informing the public about interactive environmental projects.
We've outlined the ArcGIS Online, Google Earth Engine, and Mapbox platforms in the previous paragraphs. Now, let's share a few quick tips about these tools:
ArcGIS Online: Start exploring core functionality with a developer account or a 21-day free trial.
Google Earth Engine: It is a platform that is open to application for academic and research projects, completely free of charge and has powerful analysis capabilities.
Mapbox: Offers a limited free usage quota. Provides a user-friendly learning experience thanks to its comprehensive, well-structured documentation.

Data formats (Shapefile, GeoJSON, CSV) and coordinate systems (Web Mercator, WGS84) must be compatible across platforms. For the map to function quickly and smoothly, you should use only the necessary data and avoid excessive queries.
ArcGIS caters to enterprise needs, GEE for big environmental data analysis, and Mapbox for flexible, interactive web maps. Each caters to a different need.
In light of all this, we understand that real-time mapping solutions are a common tool not only for surveyors and data analysts, but also for a wide range of users, from city managers and disaster recovery teams to software developers and environmental researchers. Platforms like ArcGIS Online, Google Earth Engine, and Mapbox offer users distinct advantages with their specialized architectures tailored to specific needs. The key is to identify the right tool for your project and leverage this power effectively with the right data structures and integrations.
If you're looking to implement a dynamic mapping application that works with real-time data in your project, the platforms and recommendations we've reviewed in this article can be helpful. Remember: maps don't just show; they guide. See you again in future articles with different scenarios, tools, and application examples!













Comments